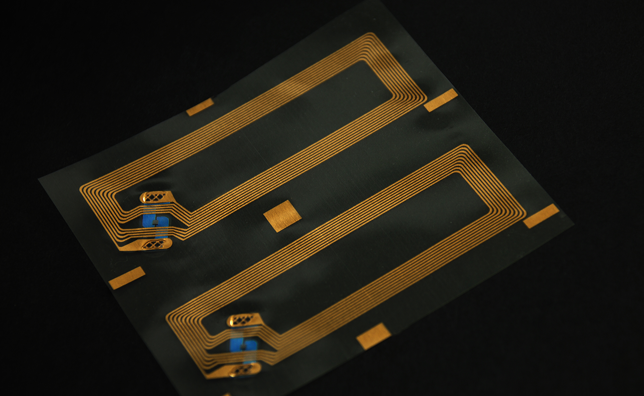
RFID tags and smart labels
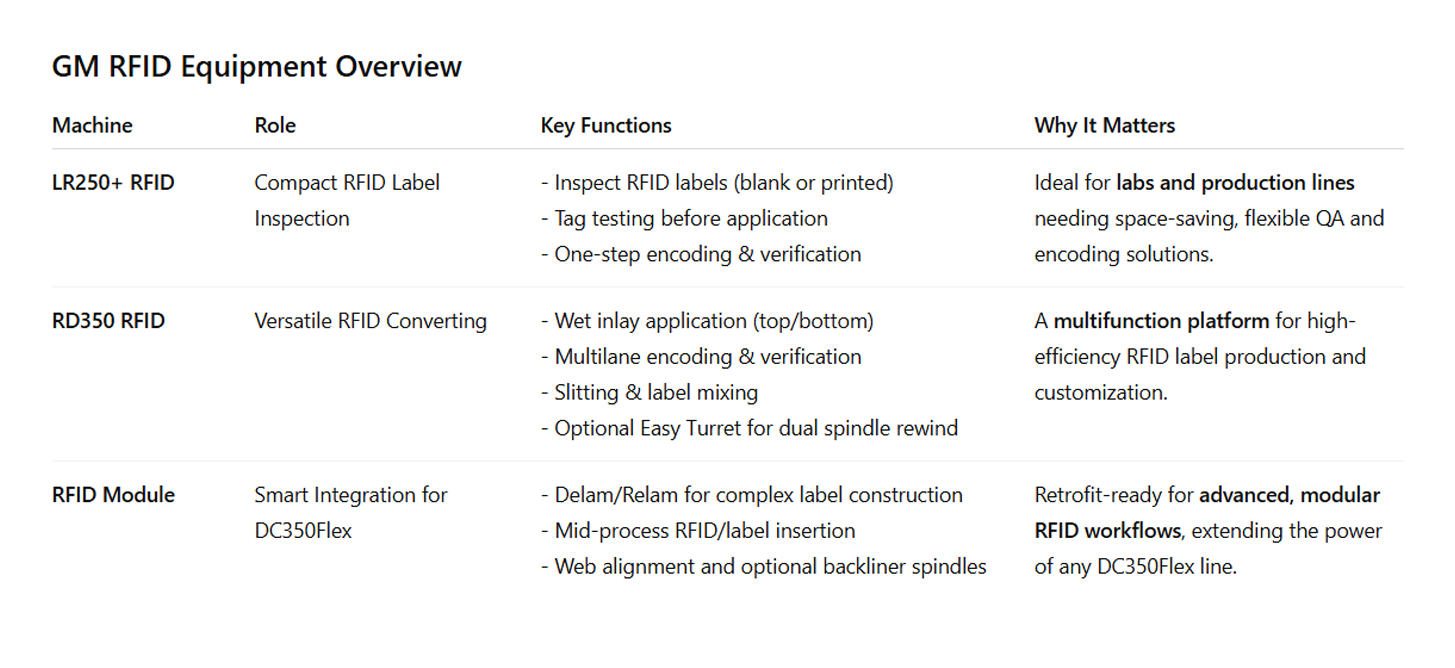
RFID Technology and Smart Labels: Enhanced by GM Technology.
The adoption of RFID technology continues to expand across industries, from logistics and healthcare to retail and manufacturing, demonstrating its capacity to drive operational efficiency, improve traceability, and transform traditional processes.
RFID tags and smart labels revolutionize identification and tracking by using integrated circuits, antennas, and substrates. At the core is the RFID inlay, which encodes essential data for wireless transmission and identification.
GM enhances this ecosystem by offering custom RFID tag and smart label finishing solutions tailored to specific application needs. From high-quality converting, laminating, and die-cutting to custom printing and encoding services, GM ensures your RFID components are not only functional but production-ready. Their expertise in precision label finishing and RFID integration bridges the gap between raw tag manufacturing and end-use implementation, accelerating deployment and maximizing ROI.